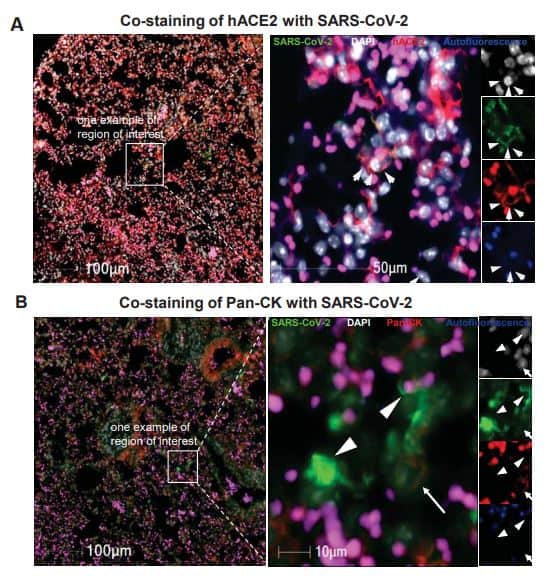
Blair, R.V., Vaccari, M., Doyle-Meyers, L.A.. et al. Acute Respiratory Distress and Cytokine Storm in Aged, SARS-CoV-2 Infected African Green Monkeys, but not in Rhesus Macaques. This article is a preprint and has not been certified by peer review. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.18.157933. SARS-CoV-2 induces a wide range of disease severity ranging from asymptomatic infection, to a life-threating illness, particularly in the elderly and persons with comorbid conditions. Among those persons with serious COVID-19 disease, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a common and often fatal presentation. Animal models of SARS-CoV-2 infection that manifest severe disease are needed to investigate the pathogenesis of COVID-19 induced ARDS and evaluate therapeutic strategies.