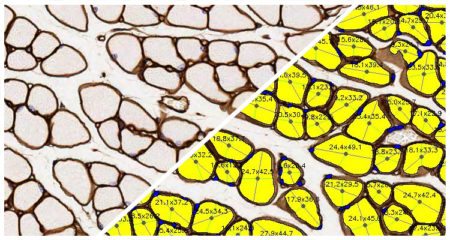
Detect and measure muscle fibers with the HALO® Muscle Fiber FL module. This module can analyze an unlimited number of fluorescent fiber or membrane dyes and reports the total fiber count as well as the average fiber diameter, perimeter length, and area. Perform in-depth analysis of individual fiber measurements with optional per-object results, including the minimum and maximum diameter, perimeter length, area, fluorescent intensity, and presence/absence of a central nucleus for each fiber.
Try it out! Click here to initiate your free proof-of-concept HALO image analysis.
Detect and measure muscle fibers with the HALO® Muscle Fiber FL module. This module can analyze an unlimited number of fluorescent fiber or membrane dyes and offers pre-trained AI-based membrane and/or nuclear segmentation for optimizing your image analysis. Gain a deeper understanding of your samples with analysis outputs including total fiber count, average fiber measurements, and per-fiber results, including the minimum and maximum Feret diameter, perimeter length, area, and presence/absence of a central nucleus. After analysis, leverage interactive markups to dynamically explore your results
Try it out! Click here to initiate your free proof-of-concept HALO image analysis.
File formats supported by the HALO image analysis platform:
- Non-proprietary (JPG, TIF, OME.TIFF)
- Nikon (ND2)
- 3D Histech (MRXS)
- Akoya (QPTIFF, component TIFF)
- Olympus / Evident (VSI)
- Hamamatsu (NDPI, NDPIS)
- Aperio (SVS, AFI)
- Zeiss (CZI)
- Leica (SCN, LIF)
- Ventana (BIF)
- Philips (iSyntax, i2Syntax)
- KFBIO (KFB, KFBF)
- DICOM (DCM*)
*whole-slide images

HALO® MASTERCLASS WEBINAR SERIES
Fall/Winter of 2020 | Indica Labs is excited to continue our HALO® Masterclass Webinar Series this autumn. Each masterclass webinar will offer a deep dive
HALO® High Impact Publications
Learn how HALO image analysis is leveraged in fields from immuno-oncology to neuroscience and infectious disease in this selection of high-impact publications.
Submit the form below to view the requested document
Publication Spotlight
The table below includes publications that cite the Muscle Fiber and Muscle Fiber FL modules.
Your publication not on the list? Drop us an email to let us know about it!
| Title | Authors | Year | Journal | Application | HALO Modules | Product |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibition of myostatin prevents microgravity-induced loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength | Smith RC, Cramer MS, Mitchell PJ, Lucchesi J, Ortega AM, Livingston EW, Ballard D, Zhang L, Hanson J, Barton K, Berens S, Credille KM, Bateman TA, Ferguson VL, Ma YL, Stodieck LS | 2020 | PLOS One | Myology | Muscle Fiber | HALO |
| Dynamic changes to lipid mediators support transitions among macrophage subtypes during muscle regeneration | Giannakis N, Sansbury BE, Patsalos A, Hays TT, Riley CO, Han X, Spite M, Nagy L | 2019 | Nature Immunology | Immunology, Myology | Muscle Fiber | HALO |
| Myostatin blockade with a fully human monoclonal antibody induces muscle hypertrophy and reverses muscle atrophy in young and aged mice | Latres E, Pangilinan J, Miloscio L, Bauerlein R, Na E, Potocky TB, Huang Y, Eckersdorff M, Rafique A, Mastaitis J, Lin C, Murphy AJ, Yancopoulos GD, Gromada J, Stitt T | 2015 | Skeletal Muscle | Myology | Muscle Fiber | HALO |
| Peripheral androgen receptor gene suppression rescues disease in mouse models of spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy | Lieberman AP, Yu Z, Murray S, Peralta R, Low A, Guo S, Yu XX, Cortes CJ, Bennett CF, Monia BP, La Spada AR, Hung G | 2014 | Cell Reports | Myology | Muscle Fiber | HALO |
| The Goto Kakizaki rat: Impact of age upon changes in cardiac and renal structure, function | Meagher P, Civitarese R, Lee X, Gordon M, Bugyei-Twum A, Desjardins J, Kabir G, Zhang Y, Kosanam H, Visram A, Leong-Poi H, Advani A, Connelly K | 2022 | PLOS ONE | Myology | Muscle Fiber | HALO |
| A growth factorñexpressing macrophage subpopulation orchestrates regenerative inflammation via GDF-15 | Patsalos A, Halasz L, Medina-Serpas M, Berger W, Daniel B, Tzerpos P, Kiss M, Nagy G, Fischer C, Simandi Z, Varga T, Nagy L | 2021 | Journal of Experimental Medicine | Muscle Fiber | HALO | |
| Low immunogenicity of LNP allows repeated administrations of CRISPR-Cas9 mRNA into skeletal muscle in mice | Kenjo E, Hozumi H, Makita Y, Iwabuchi K, Fujimoto N, Matsumoto S, Kimura M, Amano Y, Ifuku M, Naoe Y, Inukai N, Hotta A | 2021 | Nature Communications | Other | Muscle Fiber | HALO |
| Electrical impedance myography detects dystrophin-related muscle changes in mdx mice | Hiyoshi T, Zhao F, Baba R, Hirakawa T, Kuboki R, Suzuki K, Tomimatsu Y, O'Donnell P, Han S, Zach N, Nakashima M | 2023 | Research Square | Myology | Area Quantification, Muscle Fiber | HALO |
| Effects of the purified dry extract of fermented ginseng BST204 on muscle fiber regeneration | Jo S, Park Y, Chang Y, Moon J, Lee S, Lee H, Kim M, Kim D, Bae S, Park S, Yun H, You J, Im M, Han H, Kim S, Jin D | 2023 | Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports | Myology | Muscle Fiber | HALO |
| Rotator cuff muscle fibrosis can be assessed using ultrashort echo time magnetization transfer MRI with fat suppression | Chang EY, Suprana A, Tang Q, Cheng X, Fu E, Orozco E, Jerban S, Shah S, Du J, Ma Y | 2023 | NMR in Biomedicine | Fibrosis | Muscle Fiber | HALO |
| Heteroduplex oligonucleotide technology boosts oligonucleotide splice switching activity of morpholino oligomers in a Duchenne muscular dystrophy mouse model | Hasegawa J, Nagata T, Ihara K, Tanihata J, Ebihara S, Yoshida-Tanaka K, Yanagidaira M, Ohara M, Sasaki A, Nakayama M, Yamamoto S, Ishii T, Iwata-Hara R, Naito M, Miyata K, Sakaue F, Yokota T | 2024 | Nature Communications | Myology | Area Quantification, Muscle Fiber | HALO |
| Peripheral neural interfaces: Skeletal muscles are hyper-reinnervated according to the axonal capacity of the surgically rewired nerves | Tereshenko V, Dotzauer D C, Schmoll M, Harnoncourt L, Carrero Rojas G, Gfrerer L, Eberlin K R, Austen Jr. W G, Blumer R, Farina D, Aszmann O C | 2024 | Science Advances | Neuroscience | Muscle Fiber | HALO |
| Selpercatinib mitigates cancer cachexia independent of anti-tumor activity in the HT1080 tumor model | Skatri U, Gouda MA, Pandey S, Chauhan NK, Shen T, Hu X, Li M, Huang S, Subbiah V, Wu J | 2025 | Cancer Letters | Oncology | Muscle Fiber | HALO |
Related HALO Modules
Quantify expression of an unlimited number of biomarkers in any cellular compartment - membrane, nucleus or cytoplasm.
Learn MoreSeparate multiple tissue classes across a tissue using a learn-by-example approach. Can be used in conjunction with all other modules (fluorescent and brightfield) to select specific tissue classes for further analysis.
Learn MoreQuantify area, diameter, and perimeter of muscle fibers stained with laminin or other fiber membrane stains.
Learn MoreUse the arrows above to view additional related modules
Want to Learn More?
Fill out the form below to request information about any of our software products.
You can also drop us an email at info@indicalab.com
Products & Services
Interested in purchasing or learning more about our products and services? Our highly trained application scientists are a couple of clicks away.
Software Maintenance & Support Coverage
Interested in purchasing an SMS plan? We would be happy to give you a quote.
Technical Support
Need technical support? Our IT specialists are here to help.