Advanced Prostate Cancer with ATM Loss: PARP and ATR Inhibitors
Antje Neeb, et al, European Urology, 2021
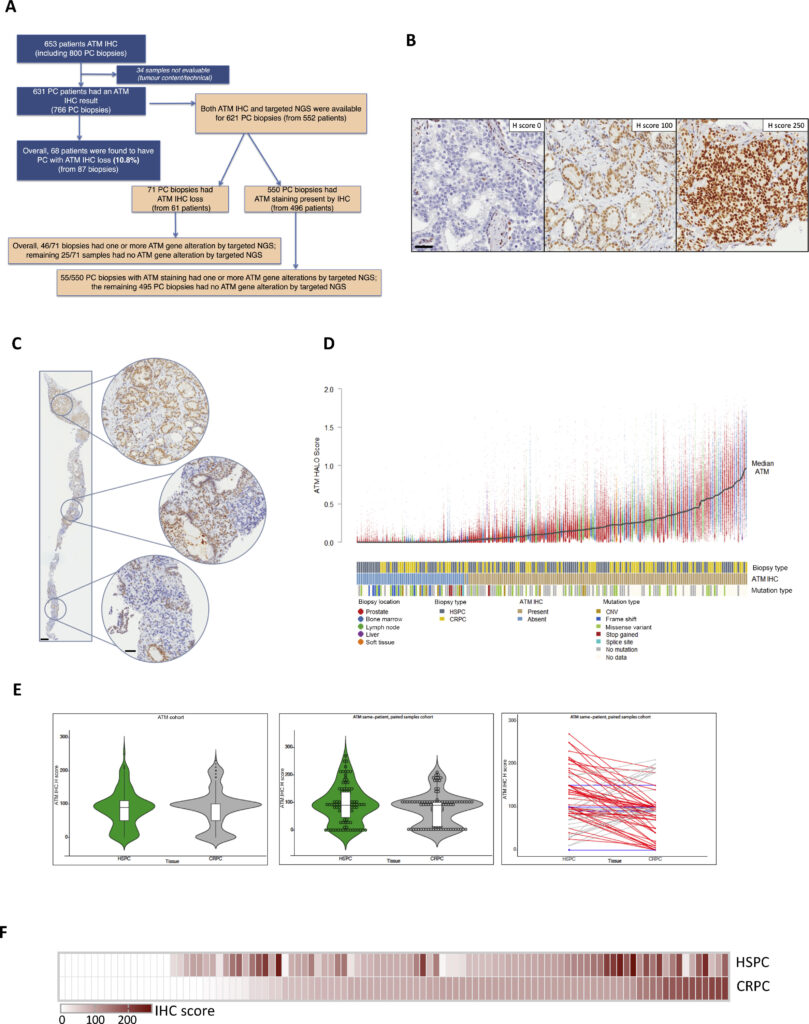
Researchers set out to evaluate the role of the ATM kinase in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) with the long-term goal of improving molecular stratification in patients. HALO and HALO AI were used in the analysis of 800 ATM immunohistochemistry samples. Neeb et al detected ATM loss by IHC in 11% of their patient cohort which was associated with increased genomic instability but was not associated with a worse outcome. An in vitro model of ATM loss showed sensitivity to ATR and PARP inhibitors, which may be further investigated in future clinical trials of patients with ATM loss.
Advanced Prostate Cancer with ATM Loss: PARP and ATR Inhibitors Read More »